
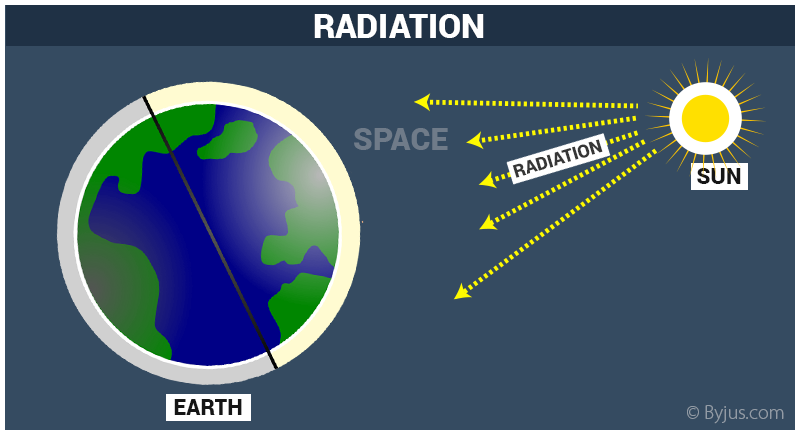
Therefore, it does not focus on a single frequency. The total solar radiation is distributed in a broad spectrum of non-uniform amplitude with the typical shape of a bell, as is typical of the spectrum of a black body with which the solar source is modeled. As a result, they reach the equatorial zone more quickly than at high latitudes. Has greater difficulty passing through the atmosphere. Ultraviolet A or UVA: They easily pass through the atmosphere, reaching the entire earth's surface. In turn, ultraviolet (UV) rays are subdivided into three types: Other types of rays: represent about 1% of the total. Ultraviolet rays (UV radiation): represent 7%. Visible rays (VI): represent 43% of radiation and provide light. Infrared rays (IR): Infrared radiation provides heat and represents 49% of solar radiation. Solar radiation is made up of the following types of radiation: On average, the value of the solar constant is 1.366 W / m2.
Electromagnetic radiation propagates in space at the speed of light (299,792 km / s).Ī singular value is the solar constant the solar constant is the amount of radiation received instantly per unit area in the outer part of the earth's atmosphere in a plane perpendicular to the solar rays. Nuclear radiation produces electromagnetic radiation at various frequencies or wavelengths. Nuclear fusion reactions take place in the solar nucleus and are the source of the Sun's energy. Likewise, solar irradiance is the power received in an instant - it is expressed in watts per square meter (W/m2) Solar irradiation is the energy received per unit area (J/m2), the power received in a given time. When we speak about the amount of solar energy reaching the surface of our planet, we use irradiance and irradiation concepts. Radioisotope thermal generators use radiant energy from a radioactive source to collect heat or even make electricity.Solar radiation definition: it is the energy emitted by the Sun in interplanetary space.The biomass created by plants can also be used in biofuels. Animals can obtain some of this chemical energy as food by eating plants, or by eating animals which eat other animals or plants. They absorb radiant energy from sunlight and transform it into useful chemical energy contained in molecules within their cells.

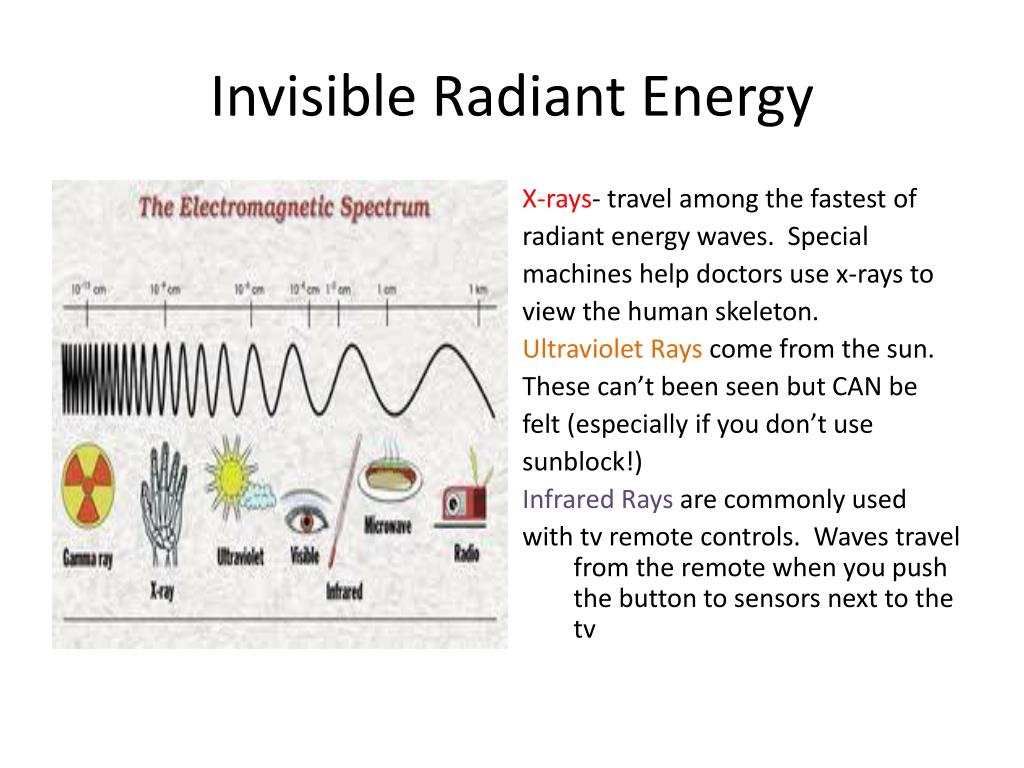
Plants are able to harness and use light energy in a process called photosynthesis. Solar power harvests radiant energy carried by the light from our sun by converting it into electricity.Ways to use collect radiant energy include: The radiant energy of a photon can span many orders of magnitude (a factor of 10 24!), but there's only a very small portion that is visible, as shown here. The electromagnetic spectrum: more energy corresponds to shorter wavelength and higher frequency since all three quantities are closely related. Photons with higher energies are found in ultraviolet rays, in x-rays, and in gamma rays.įigure 2. Photons with lower energies are found in microwaves, radio waves, and as infrared radiation (which is felt as heat). Only photons within a very small range of energies can be seen by people, commonly known as visible light. Not all radiant energy is visible (see figure 2). This electromagnetic wave can be seen in figure 1. Examples of radiant energy include the warmth that radiates from a hot stove and the warmth from direct sunlight. Because photons are so small, light energy is often measured in electron volts. Light is made of individual particles called photons, each carrying a small "packet" of energy. Practically speaking, this is the energy found in electromagnetic waves, also known as light. Radiant energy, also known as electromagnetic radiation (EMR), is energy transmitted without the movement of mass.
The electric (red) and magnetic (blue) fields are changing, causing the radiation moving to the right.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
